“You have the right to expect NHS bodies to monitor, and make efforts to
improve continuously, the quality of healthcare they commission or provide. This
includes improvements to the safety, effectiveness and experience of services” –
The NHS Constitution
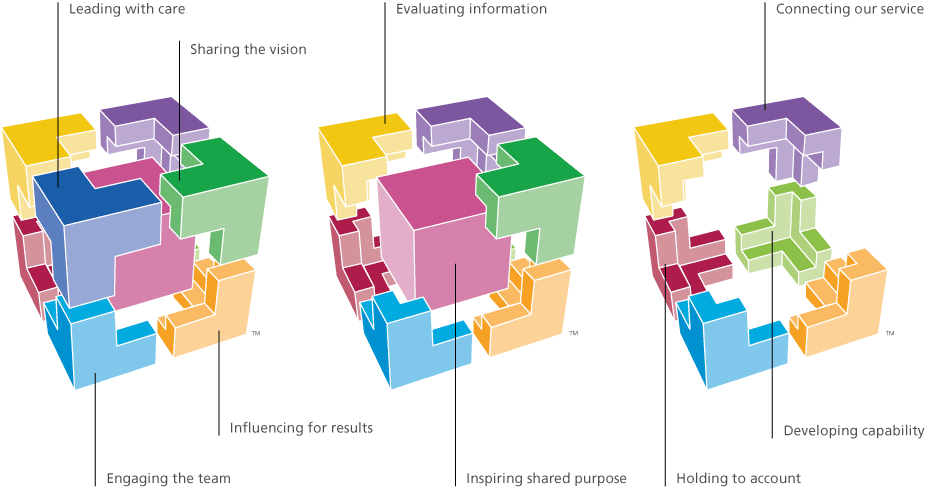
Figure 1. WHO guidelines (51)
The National Health Service (NHS) provides care for 1 million patients every 36 hours (1). This report will assess how this complex healthcare system strives to treat all patients equally and with high quality, through regulation (2).
Regulation is the ‘sustained and focused control exercised by a public agency over activities which are valued by a community’ (3). Regulation within the NHS aims to attain consistent, high quality care (4) across all services by the use of legal frameworks (5) and accountability which uses clear, simple guidance
alongside clarifying the roles and responsibilities as health-care providers (5). A large majority of NHS patients encounter the Medical imaging department and therefore it is vital to assess whether these departments are providing optimal care to these patients.
The need for regulation reform was recently publicised in the media in cases where reports of negligence within NHS services caused avoidable harm and death to multiple patients (6) (7) (8) (9) (10). These reports highlighted areas which needed vital attention in the services provided, such as improved inter-professional working, staff training and increased awareness of accountability in order to provide high-quality, equal and compassionate care, for all (6).
These reports also made it clear that current regulation and monitoring methods must be adapted and improved, primarily in structure. For example “in the case of Mid Staffordshire, the regulatory regime that allowed for overlap of functions led to a tendency for regulators to assume that the identification and resolution of non-compliance was the responsibility of someone else. Effective accountability to the public demands a simpler regime of regulation” (6)
The reports which begged for better regulation
There have been multiple cases within the NHS where patients were not treated with the care and rights that they are entitled to. These reports highlighted that increased knowledge, resources and reduced workload were key to improving care, however, effective communication was paramount (4).
Victoria Climbié was seen by multiple healthcare professionals who should have noticed she was being abused, before she was murdered. Her death sparked the formation of the Children’s Act 2004 (13) and the ‘Every Child Matters’ initiative (14). It was summarised that her abuse was not noticed due to racism; a cultural attitude of staff believing it was “not their job”; and disorganisation throughout management. Regulation ensures patients are treated equally and that staff are adequately trained and accountable to their actions.
Neglect to those with learning disabilities was highlighted with reports into the Winterbourne View care home (8) and Steven Hoskin’s death (10). These cases brought to light the importance of communication between different organisations and departments, as lives could have been saved (10) if public service workers communicated better. The CQC now monitor the appropriate usage of the Mental Health Act to safeguard those who are not mentally capable to fully look after themselves (15).
The Keogh Report(2013) investigated unacceptably high death rates at fourteen UK hospitals. This report suggested four key principles to reduce incident rates: improved patient and public participation; improved listening to the views of staff; openness and transparency and co-operation between all public service organisations (9).
The ‘straw that broke the camel’s back’, in regards to the need for better regulation, was the Francis Report(2013) (6) which investigated the monitoring of Mid Staffordshire Foundation Trust and how nacceptable practices had not been identified and acted upon. This report cried out for restructuring of
NHS regulation as the previous system wasn’t effective at ensuring patient safety and care; it tolerated a culture which accepted poor working standards from other staff and reprimanded whistleblowers. The Berwick report was a response from the Department of Health (DoH) to the Francis Report which looked at methods “to make zero harm a reality in our NHS” (16).
These inquiries stated that regulation had to be improved as, although regulation occurred in the departments which were investigated, it was not substantial or objective enough. As a result of this, better regulation, public awareness and regulatory bodies were founded (17) (18) (19) (20).
Main regulatory bodies
All regulatory bodies make use of the and statutes such as the Human Rights and Health and Safety at Work Act (23). Regulatory bodies are accountable to the Government and public for all healthcare services’ actions and try to adhere to targets and protocols set by government to optimise efficiency and care. The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (24) provides evidence-based protocols and guidelines which hospitals should adhere to, in order to set a high standard of healthcare which is accessible by all.
The Care Quality Commission (CQC) (18) is the main independent regulatory body which commissions all healthcare providers and was established by the Health and Social Care Act(2008) (17) to provide a governing body which ensures all providers of the NHS meet essential standards of quality and safety (25). Healthwatch England is an independent consumer champion for health and care which works at a local and national level as a mediator between the public and the CQC. The CQC must listen and respond to
Healthwatch England’s views on how services are being run (26).
Monitor is similar to the CQC, they regulate and provide licenses to Foundation Trusts in order to “make the health sector work for patients” (20).
The United Kingdom Accreditation Service and their sub-section, the Imaging Services Accreditation Scheme (ISAS) provides accreditation to departments who have met internationally agreed standards (27). The Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC) regulates healthcare professionals by implementing registration to those who are qualified and adhere to their professional, behavioural and health-focused guidelines (28). Those who are not registered by the HCPC are not legally allowed to work for the NHS using HCPC protected titles, such as, ‘Radiographer’ (29).
Clinical Governance is a systematic approach to improvement and development within the NHS with focus on the patient’s experience(30). Ongoing monitoring is a requirement of regulation, alongside methods such as pre-arranged and unannounced inspections, audits and patient/staff feedback to assess the quality of care that the NHS provides (31). Clinical audits are evaluations of pre-existing care using an objective, systematic review of data against explicit criteria (32). If an audit finds that the desired high quality practice, as set by legislation, is not being carried out, a plan or framework is put into place to achieve the correct standards. Frameworks can include training and education, financial incentives or improved legislation; unexpected results from an audit may also trigger new research into that area.
Inspections, carried out by all regulatory bodies, are unannounced and are performed routinely or as a response to concerns and conducted by trained inspectors alongside clinical experts and experts by experience. During inspections, facilities, equipment, staffing, care- plans and protocols are checked and discussions with service-users and staff ensures fair appraisal of the day-to-day experiences within departments (15). Regulation structures and supports the development of policies through impact assessment, where the goal is to continually improve care and efficiency (33).
Self-evaluation of healthcare professionals is crucial in attaining individual high standards of professionalism and patient care by adhering to legislation, protocol and codes of conduct, such as those set out by the Society of Radiographers and the HCPC. Continuous Professional Development is a mandatory requirement of HCPC registration (34) and its purpose is to improve the healthcare professional’s knowledge and skills. Professionals are required to adapt accordingly as research, priorities, systems and knowledge change. The HCPC regulates this every two years to ensure members are up-to-date with best practice. An individual must work within their job remit, carry out adequate training and are obligated to raise concerns if they are not satisfied with others or their own practice through whistleblowing (35).
Purpose of Regulation
“Regulation is intended to guard against quality deficiencies” (36)
Regulation’s primary purpose is to improve a health service’s quality of care, ensuring every service which it provides is completely patient centred. Accountability is an integral part of professional practice; every health service provider and their employees must be responsible, by law, for their actions.
Regulators evaluate whether a service is failing to meet set standards and if so, they can intervene with immediate termination of the service and/or disciplinary action. Regulatory bodies assess why the requirements are not being met, and what can be changed to aid improvement of the service. A common reason for failure to meet objectives is the lack of staffing or inadequate facilities, and once the regulatory bodies establish this, measures can be put in place to ensure this is no longer a problem. Regulation can also
improve knowledge, both within the work-force and publicly, so that people are more aware and qualified to deal with certain situations. An example of this is the awareness of improved infection control practice, with increased training for professionals and public advertising:
The Human Rights Act (21) states that all persons have a right to a life which is free from violence. Mistreatment and negligence in healthcare services have caused breaches of this act, where violence, humiliation and torture have necessitated public inquiries (10). All patients should be treated equally and
protocol ensures that everyone is treated by one set standard, promoting a better experience for the patient. Every hospital is required to have a Patient Advice and Liaison Service, where if the patient has not had a satisfactory experience then they have access to a non-judgemental, independent body to raise their complaints (37).
Regulation ensures that the 7 core principles of the NHS and the Government Standards of Care are being followed, and as ‘The NHS belongs to us all’ (11) patients have to right to know what care they can expect to be treated with.
Regulation in the Medical Imaging
Diagnostic “radiographers are at the heart of modern medicine” (38)
Radiographers are regulated by the HCPC and as part of their registration, all radiographers must perform best practice at all times in accordance to their codes of conduct(35). This involves a commitment to the health and safety of service users with professional competency, integrity, honesty and continued self-development especially in regards to ethics and behaviour (39).
Regulation within the medical imaging department ensures that staff treat patients autonomously, with beneficence and non-maleficence and that they use justification to assess whether the benefit of treatment outweighs any risks (40). As medical imaging staff use ionising radiation, they must ensure that they are adhering to protocol appropriately in order to reduce any harm to the patient. Auditing and inspections within the medical imaging department ensures appropriate radiation protection technique is being used and that the
best equipment available for each procedure is being used, according to protocol. Departmental protocol ensures that all staff know how to undertake all procedures and react to possible scenarios and the HCPC states that staff are to work within their remit, so if they do not feel competent at performing an examination, they should raise awareness and undertake further training. Monitoring and documentation of doses to patients and staff, with agreed acceptable limits by law, ensures optimal radiation safety and allows for
research into new imaging techniques and protocols.
Independent assessment from ISAS for medical imaging departments offers accreditation for departments who meet specific requirements in regards to clinical standards, patient experience and resources (27). The aim of ISAS is to set an international benchmark, driving departmental improvement and therefore patient and staff satisfaction. Clinical assessment promotes rapid and accurate diagnosis and treatment through monitoring of Quality Assurance methods, protocol evaluation and management of radiation safety. Appropriate facilities and resources should be available and used effectively, and there should be adequate, motivated and competent staff to accommodate demand. ISAS evaluate feedback from patients and staff to
ensure patient-focused and safe care (27). Medical Imaging departments have a high amount of interprofessional working and regulation must be in place to ensure this is done properly.
Clinical Commissioning Groups (CCG’s) have been established by NHS England and can commission Any Qualified Provider (AQP’s) to provide the best service for their patients (41). This allows the patient more choice in regards to their care, whilst being ensured the best quality of care is still provided (42). Commissioning of imaging services has implications to the NHS because, if services which they previously have provided become commissioned to AQP’s then, financially, NHS departments become disadvantaged. An example of this is if a community hospital’s imaging services are closed down and replaced with a private company. To reduce the amount of services which are commissioned away from the NHS, departments aim to increase the quality of their services and care. Regulation provides public awareness of this improvement and therefore patients are more likely to choose departments who have the best outcome after regulation. This motivates the departments to perform better for increased budgets and job security.
Excellent management is essential in the restructuring of the NHS; the Francis, Berwick and Keogh reports ll highlighted lack of leadership within the NHS (6) (9) (16). Regulation of management ensures that hospitals are primarily influenced by patient welfare and not solely motivated by financial gain, target fulfilment and political influence. The Health and Social Care Act(2012) (41) stated expectations that all hospitals will be Foundation Trusts by 2014 (43). Foundation Trusts have more power over their budget and how they spend it, which reduces the amount of political influence over NHS services (36) and also allows for more local control over what services are provided.
Advantages and Disadvantages of improved regulation to NHS and Imaging Departments
There are innumerable advantages to improved regulation within the NHS as previously mentioned. However, there are also implications of regulation.
Prevention of NHS services (such as MRI and CT scanning) being outsourced to private companies, is occasionally counteracted by the cost of meeting regulatory targets for each hospital, alongside the cost to the NHS, of performing regulation. Having inspiring leaders and management within Imaging Departments further prevents this (44). The Healthcare Leadership Model helps to incorporate a more united NHS, where employees feel valued and confident to raise any concerns.
The CQC perform spontaneous inspections, providing a true evaluation of services. ISAS, however, perform pre-discussed inspections, which is not as effective as, if departments know when inspections and audits will be performed, there is an incentive to temporarily improve services for the inspection rather than maintain high quality, patient-centred care. Once the inspection has been completed, standards may drop much below the acceptable level and this would go unnoticed.
Enforcing better regulation costs time and money, as there are multiple procedures which have to be followed such as: research, approval, sending laws to parliament, government approval and enforcement. Also, there will always be some political influence over the structure of the NHS and therefore staff satisfaction and patient care. Financial implications can also include the cost of recruiting specific people to carry out regulation, such as an audit leader.
Disagreements between regulatory bodies (such as Monitor, CQC, HCPC) regarding best practice, protocols and methods should be counteracted by having set laws and legislation – and having the DoH as the over-ruling regulatory body(18) (20). Alongside this, the NHS Confederation provide a membership body for all NHS organisations to help standardised policies and aims(25), and the NHS Trust Development Authority provides support and governance for all NHS Trusts(50) . Set laws and protocols allow both
employees and service users to know exactly where they stand and what is expected for best practice (35). This improves the meeting of targets (i.e. infection control and waiting times) and therefore staff and patient satisfaction.
The greatest influence regulation has is that neglect similar to that highlighted within the Mid-Staffordshire trust will hopefully not happen again (6). There should now be a greater acceptance to whistle blowing where unacceptable care is seen (45), and openness within the NHS (46).
Conclusion
Regulation is crucial in providing a universal standard of quality within NHS and other healthcare services for service users. When caring for any patient, their best interests are paramount; final control of healthcare should always lie with the patient, wherever possible. Healthcare systems must ensure safeguards are in place to prevent maleficence (47).
Regulation within the medical imaging departments, ensures that ionising radiation is used appropriately, according to law and protocol, and provided on a risk-benefit basis. All staff using radiation must be qualified and regulated by the HCPC to ensure that they follow best practice for radiation safety, patient care and continuous professional development (35). As medical imaging staff carry out a large majority of their work within a multidisciplinary team, interprofessional communication is a vital skill to develop.
“The law requires a fair and reasonable standard of care and competence” (48);
patient care and safety should be at the core of everything the NHS does, and
regulation ensures this.
References
1. The National Health Service. The NHS in England. [Online].; 2013 [cited2014 May 27th. Available from: http://www.nhs.uk/NHSEngland/thenhs/about/Pages/overview.aspx.
2. Walshe K. The rise of regulation in the NHS. British Medical Journal (BMJ). 2002 April; 324(7343).
3. Selznick P. Focusing Organizational Research on Regulation. In Nolls RG, editor. Regulatory Policy and the Social Sciences. Berkeley: The University of California; 1985. p. 363-367.
4. NHS. High Quality Care For All (Darzi Report). Government Document. London: Department of Health; 2008.
5. Law Commission. Regulation of Health and Social Care. [Online].; 2012 [cited 2014 May 27th. Available from: http://lawcommission.justice.gov.uk/docs/cp202_regulation_of_healthcar e_professionals_impact_assessment.pdf.
6. QC RF. Report of the Mid Staffordshire NHS Foundation Trust Public Inquiry Executive Summary. Norwich: Mid Staffordshire NHSFoundation Trust Public Inquiry; 2013.
7. House of Commons Health Committee. The Victoria Climbé Inquiry Report. London: House of Commons; 2003.
8. Department of Health. Winterbourne View Hospital: Department of health review and response. London: Department of Health; 2013.
9. KBE Keogh. Review into the quality of care and treatment provided by14 hospital results in England: overview report. London: NHS; 2013.
10. Margaret C. Flynn. The Murder of Steven Hoskin A Serious Case Review. Truro: Cornwall Adult Protection Committee; 2007.
11. The National Health Service. The NHS Constitution. Government Document. London: Department of Health; 2013.
12. Care Quality Commission. National Standards. [Online].; 2014 [cited 2014 May 27th. Available from: http://www.cqc.org.uk/public/what-are- standards/national-standards.
13. Parliament Great Britain. Children Act. Act of Parliament. London:; 2004.
14. Great Britian Treasury. Every Child Matters London: Stationary Office;2003.
15. Care Quality Commission. Monitoring the Mental Health Act. Newcastle upon Tyne: CQC; 2011/2012.
16. Department of Health. Berwick review into patient safety. London:Department of Health; 2013
17. Parliament Great Britain. Health and Social Care Act. London: Parliament; 2008.
18. CQC. Care Quality Commission. [Online].; 2008 [cited 2014 May 28th.
Available from: http://www.cqc.org.uk/. 19. Parliament Great Britain. Health and Social Care (Community Health
and Standards) Act. London: Parliament; 2003.
20. Monitor. Making the health sector work for patients. [Online].; 2003
[cited 2014 May 28th. Available from: http://www.monitor-nhsft.gov.uk/.
21. Parliament Great Britain. Human Rights Act. London: Parliament; 1998.
22. Parliament Great Britain. Mental Health Act. London: Parliament; 2007.
23. Parliament Great Britain. Health and Safety at Work Act. London: Parliament; 1974.
24. NICHE. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. [Online].;
2014 [cited 2014 May 28th. Available from: http://www.nice.org.uk/.
25. NHS Confederation. The current system of regulation. [Online].; 2013 [cited 2014 May 29th. Available from: http://www.nhsconfed.org/priorities/nhs- teforms/Regulation/Pages/Regulation.aspx.
26. Healthwatch. Healthwatch England. [Online].; 2014 [cited 2014 May 28th. Available from: http://www.healthwatch.co.uk/.
27. United Kingdom Accreditation Service. Imaging Services Accreditation
Scheme (ISAS). [Online].; 2014 [cited 2014 May 29th. Available from: http://www.isas-uk.org/default.shtml.
28. HCPC. Health and care professions council. [Online].; 2014 [cited 2014
May 29th. Available from: http://www.hpc-uk.org/.
29. Parliament Great Britain. The Health Professions Order. London:Parliament; 2001.
30. Department of Health. Clinical Governance. [Online].; 2010 [cited 2014]
May 30th. Available from: http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/+/www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publichealth/Patientsafety/Clinicalgovernance/index.htm.
31. Scally GDL. Clinical governance and the drive for quality improvement in
the new NHS in England. British Medical Journal. 1998 July; 317(7150).
32. Department of Health. National Clinical Audit Advisory Group (NCAAG). [Online].; 2009 [cited 2014 May 30th. Available from: http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/+/www.dh.gov.uk/ab/NCAAG/DH_099788.
33. European Commission. Impact Assessment. [Online].; 2014 [cited 2014 May 30th. Available from: http://ec.europa.eu/smart-regulation/impact/index_en.htm.
34. HCPC. Standards of conduct, performance and ethics. London: HCPC; 2012.
35. HCPC. Standards of proficiency Radiographers. London: HCPC; 2012.
36. The King's fund. How to Regulate Health Care in England. London: The King's Fund; 2006.
37. NHS Choices. What is PALS? [Online].; 2013 [cited 2014 April 1st.Available from: http://www.nhs.uk/chq/Pages/1082.aspx?CategoryID=68.
38. Society of Radiographers. A career in radiography. [Online].; 2014 [cited 2014 April 1st. Available from: http://www.sor.org/about- radiography/career-radiography.
39. Society of Radiographers. Code of Professional Conduct. London:; 2013.
40. Beauchamp TCJ. Principles of Biomedical ethics Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2001.
41. Parliament Great Britain. Health and Social Care Act. London:Parliament; 2012.
42. NHS Choices. Clinical Commissioning Groups (CCG) and how they perform. [Online].; 2014 [cited 2014 April 1st]. Available from: http://www.nhs.uk/nhsengland/thenhs/about/pages/ccg-outcomes.aspx.
43. British Medical Association. Understanding the reforms. NHS trusts and foundation trusts. London: BMA; 2013.
44. Snelling I. The development of regulation of acute hospital in England: leadership challenges. Leadership in Health Services. 2010; 23(2). 45. Department of Health. No Secrets: guidance on protecting vulnerable
adults in care. London: Department of Health; 2000.
46. Medical Protection Society. A culture of openness The MPS perspective. London: Medical Protection Society; 2009.
47. Gosney M. Safeguarding Vulnerable Older People (Abuse and Neglect).London: British Geriatrics Society Policy Committee; 2009.
48. Shenoy G. Law Demands "Care" - Not "Cure". Journal of Gynecological Endoscopy and Surgery. 2009 Jul-Dec; 1(2).
49. Civil Society. CPR Publicity Advert. [Online].; 2014. Available from: http://www.civilsociety.co.uk/fundraising/news/content/12092/bhfs_hard_and_fast_cpr_ad_overcomes_public_complaints.
50. Trust Development Authority [Online]. 2014 [cited 2014 April 1st.] Available from: http://www.ntda.nhs.uk/
51. NHS Leadership Academy [Online]. 2014 The Healthcare Leadership Model [cited 2014 April 1st.] Available from:http://www.leadershipacademy.nhs.uk/discover/leadershipmodel/